Table of Contents
Public Cloud Private Cloud or Hybrid Cloud Whats the Difference
Cloud computing has evolved from a niche option to the industry standard for managing IT. The most common question nowadays is whether to use a public, private, or hybrid cloud.
Today, hybrid technology is gaining a lot of traction. Let’s quickly go through the differences between the three types of clouds to assist you in better comprehending the hybrid cloud.
Understanding your deployment options—Public cloud, private cloud & hybrid cloud?
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to cloud computing. Various cloud computing models, types, and services have emerged to satisfy the continuously changing technology needs of businesses.
There are three ways of implementing cloud services: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. The requirements of your firm will dictate the deployment approach you select.
- Public Cloud:
The public cloud is what most people think of when they think of the cloud. While the first program to be hosted over the internet was software as a service (SaaS), today’s public cloud can include applications, infrastructure, or data storage provided by a third-party source. It’s also useful to consider each of them separately.
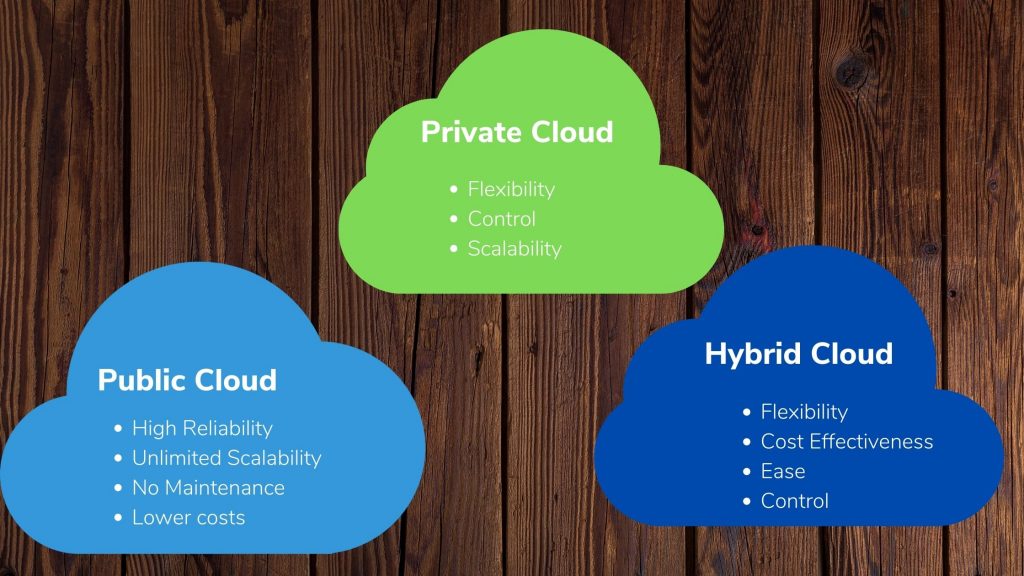
Advantages of Public Clouds:
- High Reliability: An extensive network of servers ensures that there will be no outages.
- Unlimited Scalability: To fulfill your company’s needs, on-demand resources are accessible.
- No Maintenance: Maintenance is handled by your service provider.
- Lower costs: There’s no need to buy any hardware or software, and you pay for what you use.
2. Private Cloud:
The “private cloud” appears to be quite similar to what we used to refer to as an on-premises data center. The distinction is that, like the public cloud, you organize your infrastructure using virtualization, software, and automation. While the private cloud provides the same flexibility as the public cloud, it allows you more control over security, data privacy, and compliance.
Advantages of a Private Cloud:
- Flexibility: Your company’s cloud environment can be customized to meet specific business requirements.
- Control: Higher levels of control and privacy are achievable when resources are not shared with others.
- Scalability: When compared to on-premises infrastructure, private clouds often provide higher scalability.
3. Hybrid Cloud:
Hybrid cloud has a wide range of definitions because it began as a marketing term. Some people think of it as a way to mix and match your apps, data, and infrastructure. For instance, you may store your data in a private cloud while operating your program in a public cloud. Others see it as the utilization of several cloud services coordinated to function together. The crucial point is that this method focuses on adaptability and a best-of-breed approach rather than a binary either-or policy for public vs. private cloud, which is why it’s quickly becoming the most popular cloud posture.
Advantages of The Hybrid Cloud:
- Flexibility: You can use extra resources on the public cloud when you require additional capacity/resources.
- Cost-effectiveness: You only pay for extra computing power when you need it, given the option to scale to the public cloud.
- Ease: Transitioning to the cloud does not have to be a daunting task because workloads may be phased in overtime.
- Control: Your company can retain a private infrastructure for sensitive assets or applications that demand low latency.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Where can I discover out more about the different types of cloud services?
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), serverless computing, and software as a service are the four main types of cloud computing services (SaaS). Because they build on top of one another, they’re sometimes referred to as the cloud computing “stack.”
2. What is infrastructure as a service (IaaS)?
The most basic type of cloud computing service is this. You rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, and operating systems—on a pay-as-you-go basis from a cloud provider with IaaS.
3. What is the platform as a service (PaaS)?
Cloud computing services that provide an on-demand environment for designing, testing, delivering, and maintaining software applications are called platform as a service. PaaS was created to make it easier for developers to construct web or mobile apps rapidly without worrying about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, network, and databases.
What is serverless computing?
Serverless computing, which overlaps with PaaS, focuses on developing app functionality without constantly managing the servers and infrastructure required. The cloud provider handles setup, capacity planning, and server management. Serverless architectures are scalable and event-driven, meaning they only use resources when a specified function or trigger occurs.
What is a software as a service (SaaS)?
Software as a service (SaaS) distributes software programs on-demand and usually by subscription via the Internet. SaaS allows cloud providers to host and manage software applications and underlying infrastructure and handle software upgrades and security patches. Users access the app over the Internet, commonly through a web browser on their phone, tablet, or computer.
Read More:



