Introduction
Cloud computing has brought about a transformation in the manner in which both businesses and individuals handle and process data. It presents a wide spectrum of services that can be customized to cater to specific requirements, rendering it a dynamic and adaptable solution suitable for an extensive array of applications. At the heart of cloud computing lie three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). While these three models are frequently employed in isolation, their genuine potential manifests when they are amalgamated. Within this article, we will delve into the concept of integrating these services and how their synergy unveils a realm of possibilities for both businesses and individuals.
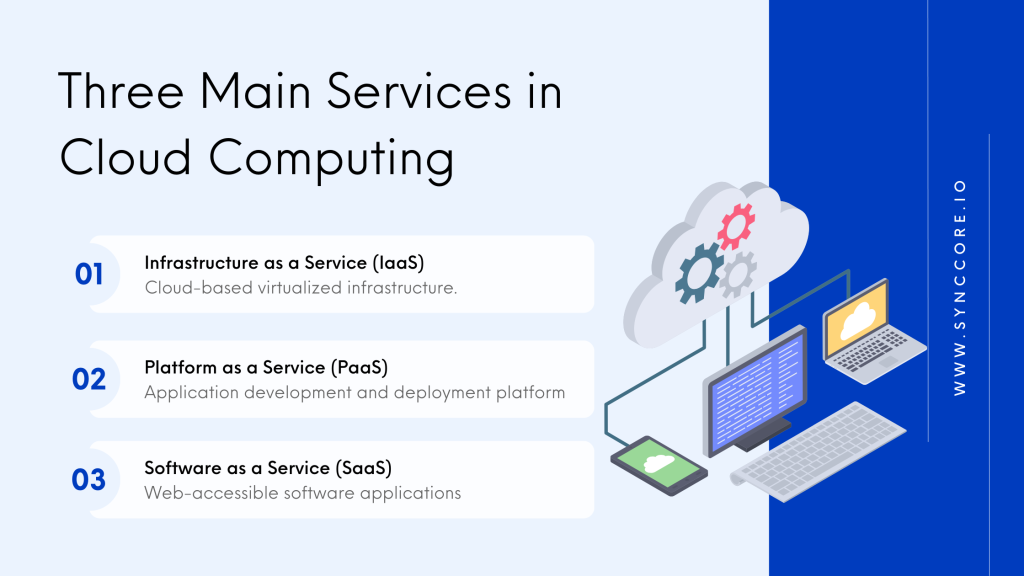
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) IaaS, the foundational layer of cloud computing, delivers virtualized computing resources via the Internet. It encompasses services such as virtual machines, storage, and networking. IaaS enables users to rent IT infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis, eliminating the necessity for physical hardware and curtailing expenses linked to maintenance and upgrades.
IaaS users enjoy the freedom to scale resources as needed, a boon for businesses with fluctuating demands. It sets the stage for amalgamating cloud services by providing the essential hardware foundation upon which other services can be constructed.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) PaaS builds upon IaaS by providing a more comprehensive development and deployment environment. It encompasses tools and services for application development, database management, and testing. PaaS empowers developers to concentrate on coding rather than managing infrastructure, rendering it an excellent choice for the rapid creation and deployment of applications.
The fusion of IaaS and PaaS generates synergy, ensuring that the infrastructure is primed for seamless application hosting. This synergy expedites the development and deployment processes, rendering them more efficient and cost-effective. Developers can leverage PaaS to fabricate and deploy applications on a scalable infrastructure without concerns about the underlying hardware and software stack.
Software as a Service (SaaS) SaaS constitutes the topmost layer of cloud computing and provides readily usable software applications accessible via the Internet. It extends a wide spectrum of tools and services, ranging from email and office suites to customer relationship management (CRM) and project management software. SaaS is user-friendly and cost-effective, eradicating the necessity of procuring, installing, and maintaining software on individual devices.
When entwined with IaaS and PaaS, SaaS optimizes the benefits of the scalable infrastructure and streamlined development processes. This amalgamation presents businesses with opportunities to craft custom applications or meld existing SaaS solutions with their infrastructure, enriching productivity and efficiency.
Integrating the Three Services
The synergistic effect stemming from the amalgamation of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS can exert a profound influence on various facets of cloud computing:
Cost Rationalization: IaaS’s pay-as-you-go model assures resource optimization, while PaaS and SaaS aid in lowering software and development expenses. This amalgamation maximizes cost-effectiveness.
Scalability: IaaS establishes the basis for upscaling or downscaling, with PaaS and SaaS seamlessly aligning with such infrastructure to ensure uninterrupted availability of applications and services, irrespective of demand fluctuations.
Time-to-Market: PaaS simplifies the development and deployment phases, curbing the time required for bringing applications to market. The streamlined development process hastens the integration or development of SaaS solutions.
Flexibility: The conjoint utilization of these services enables the creation of customized solutions tailored to meet the distinctive requirements of businesses and individuals.
Risk Mitigation: With cloud services managed by providers, businesses can concentrate on their core competencies, with providers handling security, compliance, and infrastructure upkeep.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has evolved into a cornerstone of contemporary IT infrastructure, supplying a range of services amenable to customization to satisfy specific demands. While Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service are formidable on their own, their amalgamation forges synergy that unlocks a universe of possibilities for businesses and individuals.
Through the integration of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, organizations can pare costs, adapt with ease, expedite time-to-market, and fashion flexible and bespoke solutions. This synergy fosters an approach to cloud computing that is more efficient, cost-effective, and productive, ensuring that the full potential of the cloud is harnessed to fulfill the ever-changing requirements of the digital era.



